Some users bought 48A LEVEL 2 EV Charger for electric vehicles and take it for granted that they can use 48A to charge their electric car. However, in the actual use process, they will encounter their own situations. The most important situation is whether the on-board charger of electric vehicles supports 48A charging.
Let's look at the charging power corresponding to each voltage, because sometimes the car manufacturer will not directly charge the charging current, but the charging power. If the user is in the United States and Canada, then the car can reach the rated power output with the support of the car. If the user is in Japan, South Korea or Taiwan,China, the car also adopts the American standard design, but the voltage is not up to the 240V input of the American grid, only 220V, then the power will not reach the designed rated power.
|
Input Voltage |
Input Currrent |
Output Power |
|
240V |
32A |
7.68kW |
|
240V |
40A |
9.6kW |
|
240V |
48A |
11.52kW |
|
220V |
32A |
7.04kW |
|
220V |
40A |
8.8kW |
|
220V |
48A |
10.56kW |
In some countries, people don't have level 2 power (240V) input , they only have 220V, like Japan, South Korea, their electric vehicles are also designing with SAE standard (Type 1), but their electricity system is not same with the United States or Canada, they only have 220V power, so if they buy 48A EV Charger, it can't reach 11.5 KW.
What is on Board Charger?
Having said the power supply system, let's take a look at the most important part, the on-board charger for electric vehicles, and see how this process works.
What is on board Charger?
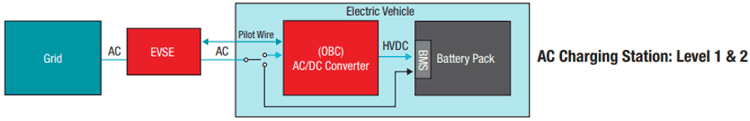
On-board charger(OBC) is a device that convert ac power from any ac source into the practical dc form. It is usually mounted inside the vehicle and it’s main function is power conversion. Hence, on-board chargers provides the advantage of charging the electric vehicle using the power outlet at our homes itself. In addition, it also eliminates the need for buying any extra equipment for power conversion.

In AC charging level 1 and level 2, the AC power from the grid is converted to DC power by the OBC to charge the battery via the Battery Management System(BMS). The voltage and current regulation is performed by the OBC. In addition, the disadvantage of AC charging is as its charging time increases, the power output becomes low.
The charging rate, or required input current, is determined by the EV itself in AC chargers. Because not all electric vehicles (EVs) require the same amount of input charging current, the AC Charger must communicate with the EV to determine the required input current and establish a handshake before charging can commence. This communication is referred to as Pilot wire communication. The Pilot wire identifies the type of charger attached to the EV and sets the OBC’s required input current.
Type of on Board Charger
There are mainly two types of on-board chargers :
- Single phase On-board Charger
- Three phase On-board Charger
The standard AVID charger has an output of either 7.3 kW if it uses only one phase or 22 kW if it uses three phases. The charger is also able to detect whether it will be able to use only one phase or three. When connected to a home AC station, which will also have an output of 22 kW, then the charging time will depend only on the capacity of the battery.
The voltage that this on-board charger can accept is 110 - 260 V AC in the case of connection to only one phase (and 360 - 440V in the case of using three phases). The output voltage that goes to the battery is in the range of 450 - 850 V.
Why my 48A EV Charger only worked 8.8 kw?
Recently, we have client who purhcased 48A Level 2 EV Charger, he has a American version of Bezn EQS to test the EV Charger. on the display, he on can see 8.8 kw charging, he is quite confused and conatct us. And we googled the EQS, and found below information:

The original link is EQS: Charging Ecosystem (mbusa.com)
We can see from the official information of Benz, the Maximum rate of Level 2 charging is 9.6kw. Let's back to the first table, which means at 240V input, it only supports Maximum 40 Amp charging. Here has one condition, that the input voltage is "240V". Did he has 240V in their house? The answer is "NO", only 220V input voltage avaible in his house, because he is not in the United States or Canada. So let's go back to above table, 220V input * 40A = 8.8 kw.
So the reason why a 48A level 2 EV Charger only charge at 8.8kw , would you know now?
Post time: Dec-19-2022




