The power of charging piles varies from 1kW to 500kW. Generally, the power levels of common charging piles include 3kW portable piles (AC); 7/11kW wall-mounted Wallbox (AC), 22/43kW operating AC pole piles, and 20-350 or even 500kW direct current (DC) piles.
The (maximum) power of the charging pile is the maximum possible power it can provide for the battery. The algorithm is voltage (V) x current (A), and the three-phase is multiplied by 3. 1.7/3.7kW refers to single-phase power supply (110-120V Or 230-240V) charging pile with a maximum current of 16A, 7kW/11kW/22kW refer to charging piles with single-phase power supply of 32A and three-phase power supply of 16/32A respectively. Voltage is relatively easy to understand. Household voltage standards in various countries, and current are generally the standards of existing electrical infrastructure (sockets, cables, insurance, power distribution equipment, etc.). The market in North America, especially the United States, is quite special. There are many types of sockets in American households (the shape, voltage, and current of NEMA sockets). Therefore, the power levels of AC charging piles in American households are more abundant, and we will not discuss them here.
The power of the DC pile mainly depends on the internal power module (internal parallel connection). At present, there are 25/30kW modules in the mainstream, so the power of the DC pile is a multiple of the power of the above modules. However, it is also considered to match the charging power of electric vehicle batteries, so 50/100/120kW DC charging piles are very common on the market.
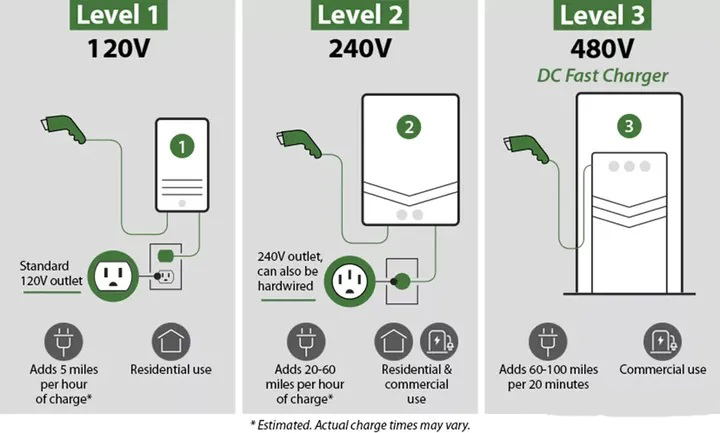
There are different classifications for electric vehicle charging equipment in the United States/Europe. The United States generally uses Level 1/2/3 to classify; while outside the United States (Europe) generally uses Mode 1/2/3/4 to distinguish.
Level 1/2/3 is mainly to distinguish the voltage of the input terminal of the charging pile. Level 1 refers to the charging pile directly powered by the American household plug (single-phase) 120V, and the power is generally 1.4kW to 1.9kW; Level 2 refers to the charging pile powered by the American household plug High-voltage 208/230V (Europe)/240V AC charging piles have relatively high power, 3kW-19.2kW; Level 3 refers to DC charging piles.
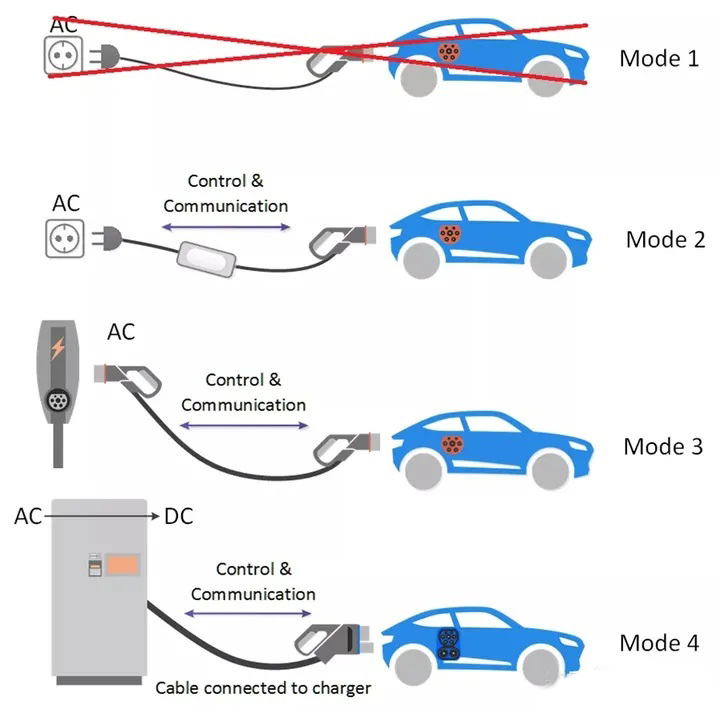
The classification of Mode 1/2/3/4 mainly depends on whether there is communication between the charging pile and the electric vehicle.
Mode 1 means that the wires are used to charge the car. One end is a common plug connected to the wall socket, and the other end is the charging plug on the car. There is no communication between the car and the charging device (there is no device in fact, only the charging cable and plug). Now many countries Charging of electric vehicles in Mode 1 mode is prohibited.
Mode 2 refers to a portable AC charging pile with non-fixed installation and vehicle-to-pile communication, and the charging process of the vehicle pile has communication;
Mode 3 refers to other AC charging piles that are fixedly installed (wall-mounted or upright) with vehicle-to-pile communication;
Mode 4 refers specifically to fixed-installed DC piles, and there must be vehicle-to-pile communication.
Post time: Aug-04-2023